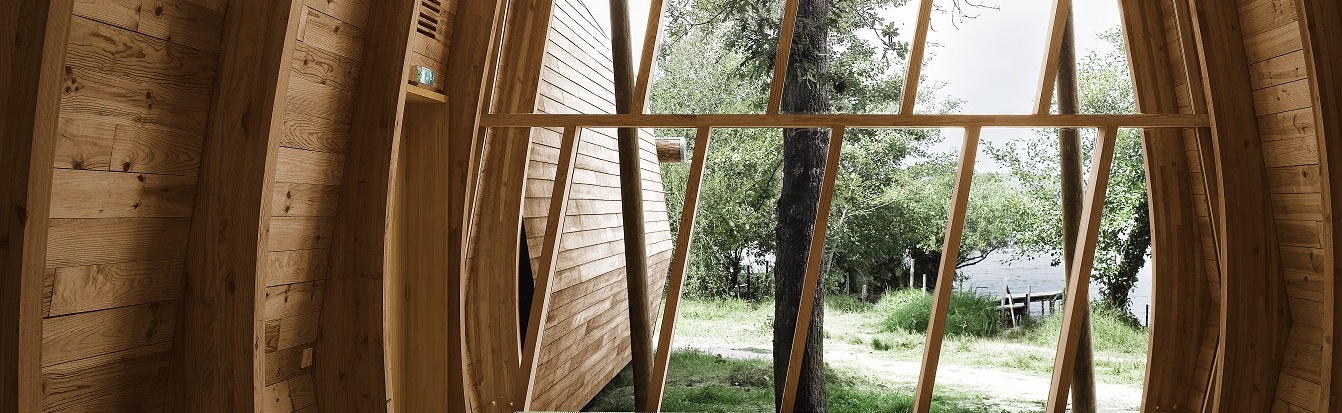
The pine industry
Thanks to its diverse range of applications, French pine generates significant industrial activity.
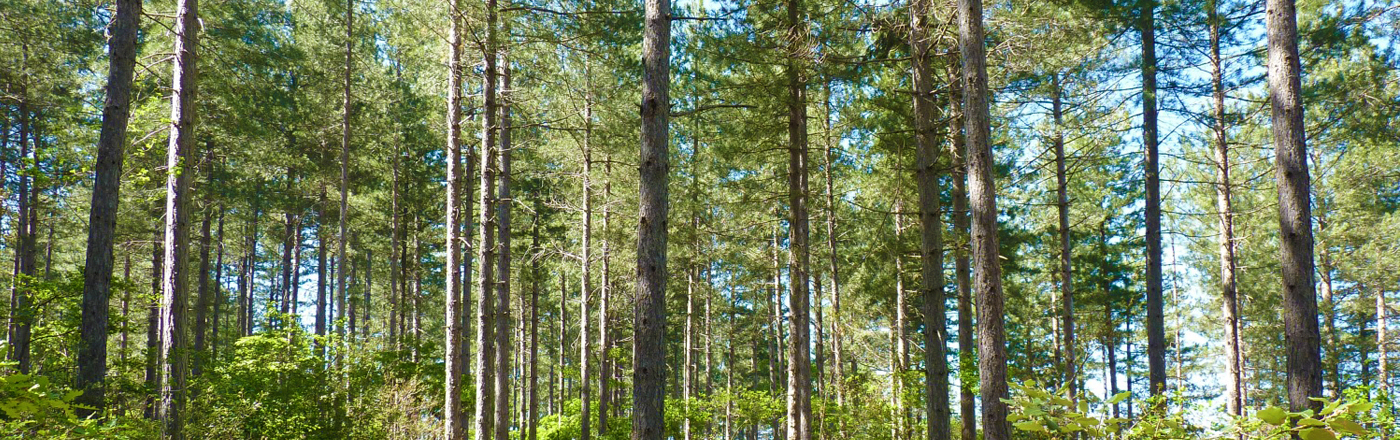
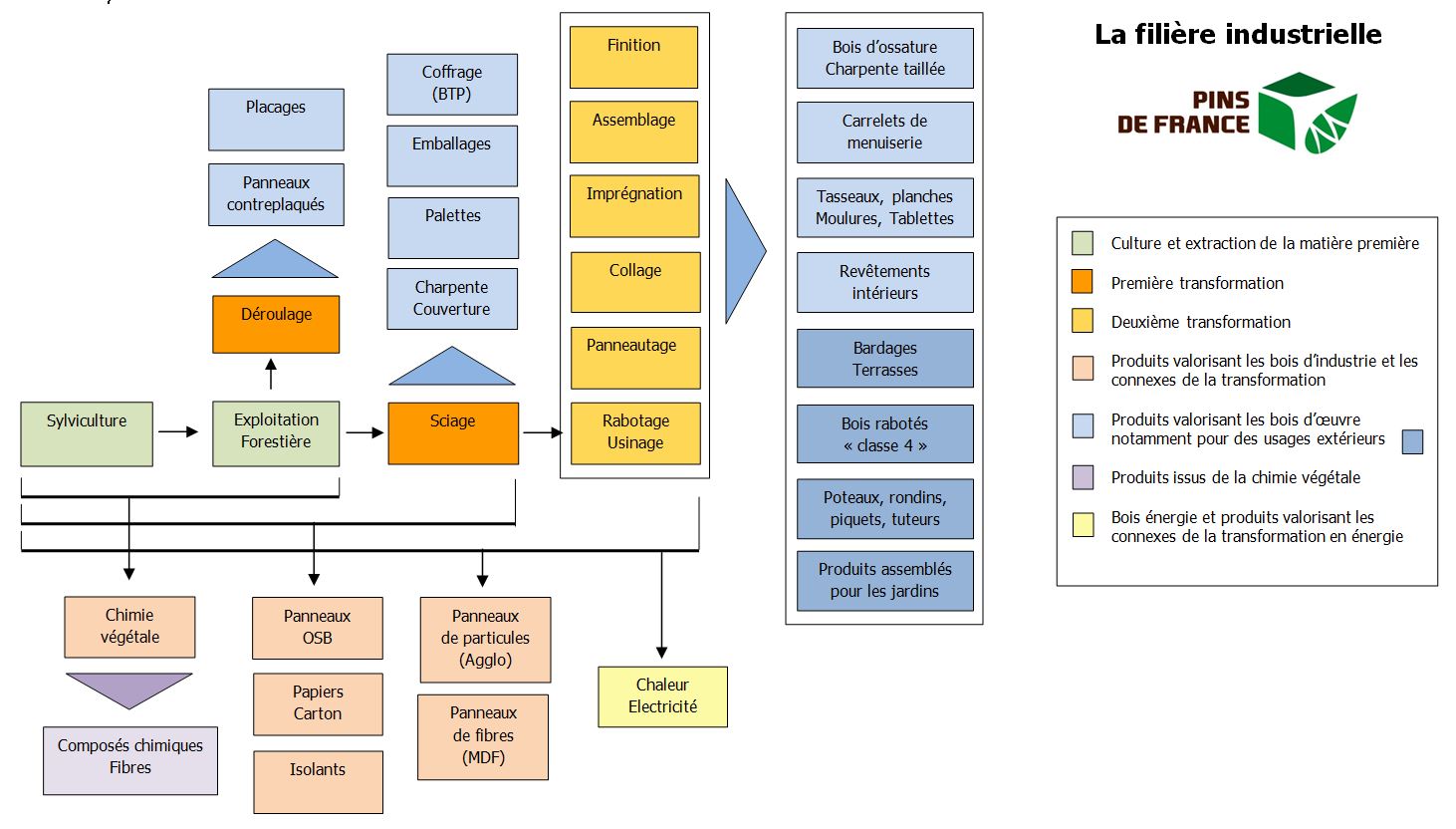
This begins with silviculture, the practice of germinating and growing trees.
Forest nurserymen supply young plants to landowners who want to plant trees.
In existing forests, regeneration is a natural process, so maintenance and operational practices need to be adapted accordingly.
Throughout the entire pine growing period, foresters survey the forests in order to provide the care needed to produce high-quality timber. This includes protecting the trees against animals, pruning, slashing, getting rid of dead wood, and selecting individual pines. Timber from silviculture work often has a small diameter but can be used for fuelwood or wood processing.
The first harvests then begin. This is when we use the term logging. The pine trees are selectively cut down, before being de-branched on the spot and occasionally even chopped up into billions of pieces. Some of them are also left as logs, depending on the practices of individual regions and the local timber needs.
The branches and the upper part of the tree (the crown) are normally used for fuelwood or in plant chemistry to extract its chemical components.
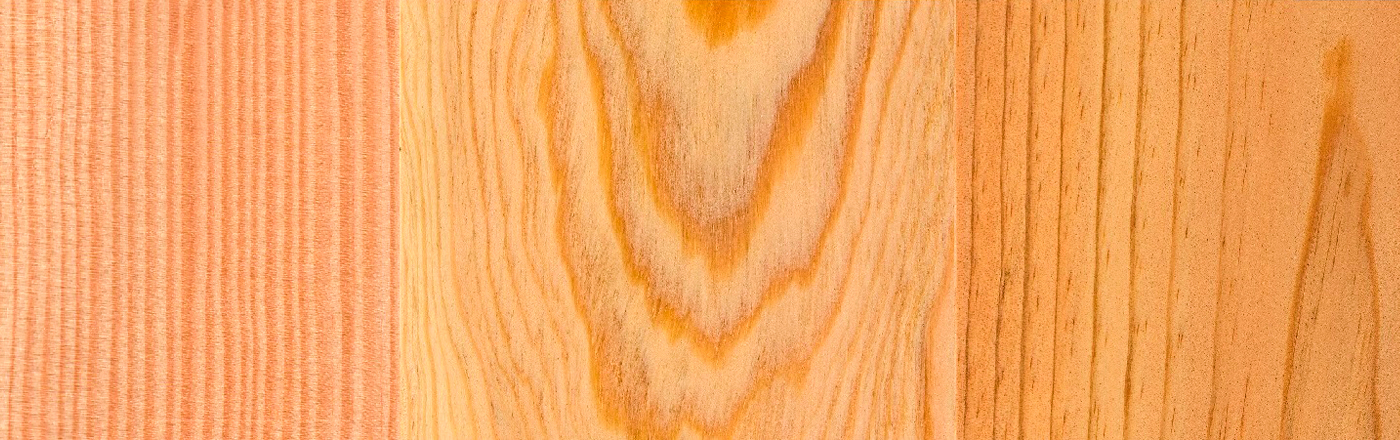
Depending on the quality of the wood, the same pine log may be used for timber- for sawing or veneering - and for wood processing, crushing, heating or electricity.
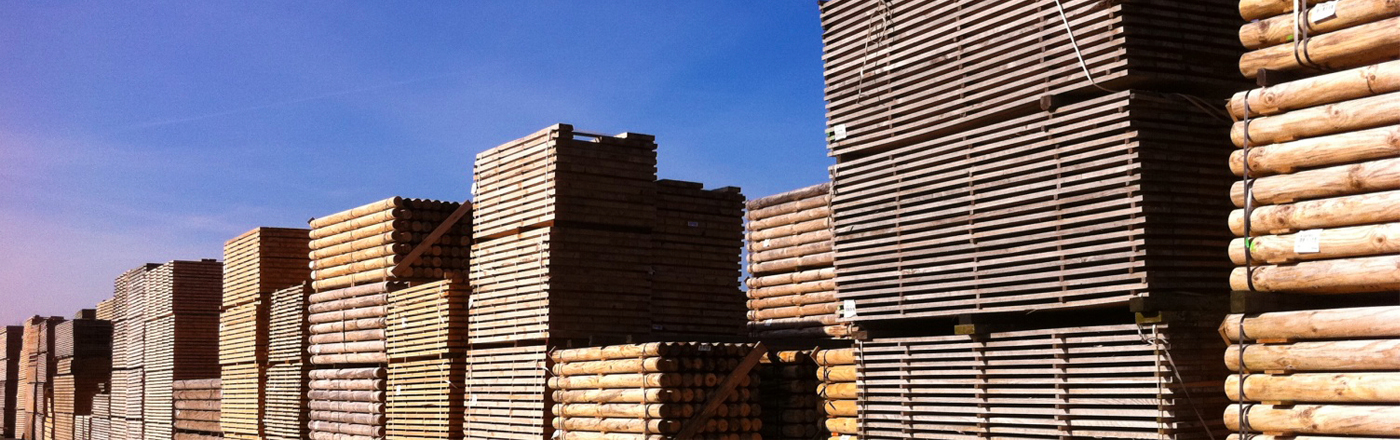
The lowest part of the tree is normally sent to plywood manufacturers for veneering because this part has less knots on its surface. The middle part is sent to the sawmill to be turned into products used in construction, design and logistics. We refer to primary processing for the sawing process itself and secondary processing for the processing stages that follow. These latter stages add high value to the product and include finishing work.
Depending on the quality of the sawn wood, the pine either goes straight through secondary processing, or is used in its current form for manufacturing pallets and boxes, and for producing formwork and supports (shoring) in construction and public works.
Crushing involves reducing the pine wood to particles and/or fibres. These can be bigger or smaller depending on the intended use and the "crushing" process chosen. Many businesses make use of this crushed wood, including particleboard manufacturers (Agglo), fibreboard manufacturers (MDF), OSB board manufacturers (Triply), insulation board manufacturers (wood wool and rigid boards) and manufacturers of pulp and paper. Depending on the type of product they manufacture, these industries also use sawing and thicknessing related wood products, including wood plates, shavings and sawdust.
Secondary processing involves several different industries and activities. Joining is one example. The wood is mechanically sorted for use in structural joining, including timber beams and finger-jointed wall framework. The wood is also visually sorted to eliminate any peculiarities, for use in cosmetic joining including glued laminated wood blocks and finger-jointed panels made of knot free pine.
The main secondary processing activity is thicknessing, which involves cleaning and smoothing the surface of the pine whilst giving it a shape and profile. This process creates products such as panelling, cladding, terraces, and moulding.
There is another essential process the pine has to undergo which allows the wood to be used outdoors and even in contact with the ground. This is called autoclave pressure impregnation.
Some wood sections intended for decorative use will undergo a finishing process (varnish, paint, saturator, oil, etc.). Many French pine businesses have automated production lines for finishing panels, parquet floors and cladding.
The French pine industry therefore pools a vast amount of expertise and probably represents over 100,000 jobs in France.